5 min read
Meeting the New, AI-Enabled Face of Risk
When we introduced our OmniNet Bridge solution in 2014—known to many of you as My Digital Shield—it represented the next generation of network...

The following transcript is from a presentation made to the Montana 9th Judicial District on June 7th, 2019 for CLE credits in technology. Charts and data use a variety of sources including Reuters, Cybersecurity Ventures, Verizon, F-Secure, CB Insights, Pitchbook, and others.

Hi, my name is Brad Deflin, I'm president and CEO of Total Digital Security, and I'm pleased to be here with you to present "Cybersecurity Simplified." Today's presentation is a compilation from my work in the field compressed to a very short 11 and a half minutes. It includes industry data, my experiential knowledge and insights, and our extensive library of data collected over the years.
While cyber risk and digital security are complex, dynamic issues today, I have three goals in my effort to simplify the topic as much as I can over the next 11 and a half minutes. My three goals include;
I'll take a two-track approach. First, we will focus on understanding the risk. Second, we'll look at mitigating the risk using innovative technology that's available today. So, let's look at understanding the risk first.
In digital security, it is becoming increasingly important to understand the risk at hand. So, for this part will look at these four key components of cyber risk;
Let's start with motives.
We'll break attack motives down to four categories:
We'll look at this mix based on these four motives since 2015. Now, let's look at cybercrime as a percentage of all activity against the other three motives.
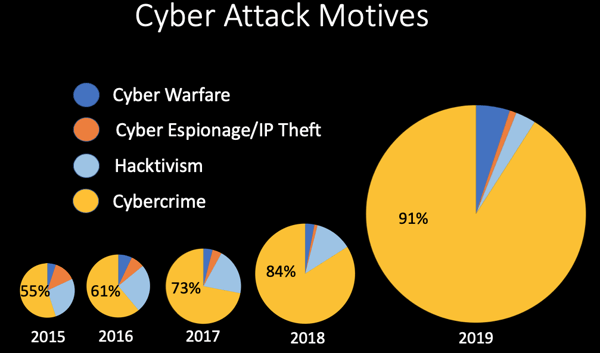
In 2015, you'll see for the first time cybercrime accounted for over half of all cyberattack activity after decades of being just a small fraction of the overall activity. By 2016, the number is 61 percent. In 2017, it goes to 72 percent, and in 2018, cybercrime amounted to over 84% of all cyber attack activity. 2019 is on track for cybercrime representing over 90% of all cyberattack activity. Here's the takeaway; while crime for profit (the yellow slices) have quickly grown to be the dominant motive behind attacks, look at the increase in the volume of attacks. The overall size of the pie from 2015 to 2018 there has been a massive increase in activity and damages, and it's led by cybercrime for profit.
That's a look at attack motives. Now let's go to attack targets.
Starting at the top of a pyramid chart with nation-states, the attack target amounts to just about 5 to 10% of the activity with North Korea, China, Russia, Iran, and of course the US and UK being top targets for nation-state attacks.
The middle layer of the chart represents targeted attacks those that are engineered with a specific target in mind and to date have been large public and private enterprises and organizations. These attacks represent about 10 to 15 percent of all activity.
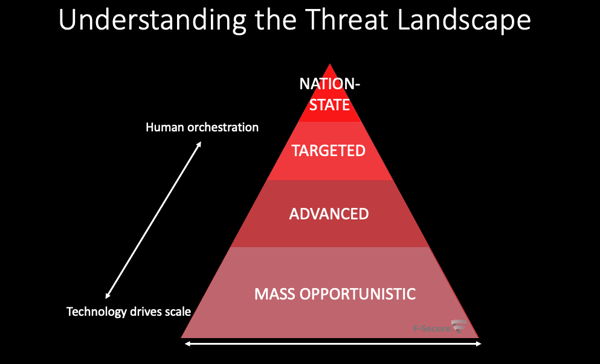
The base of the pyramid is where the action is. It's called mass-opportunistic attacks, and it's where 80% of cyberattack damages are taking place. The targets of these attacks are individuals and personal technology more than IT departments and servers its small businesses, professional practitioners, and unprotected devices with less aware users, including more and more our private lives, family members, homes, and home offices.
This brings us to a major theme of today's presentation: the personalization of cyber risk.
Where it was once exclusively about institutions and black-hat activity, like we saw in attack motives and attack targets, the Internet has democratized cyber risk and made it a very personal and individual problem. In "Understanding Cyber Risk" we've covered motives and targets, and now we'll look at attack damages and perpetrators.
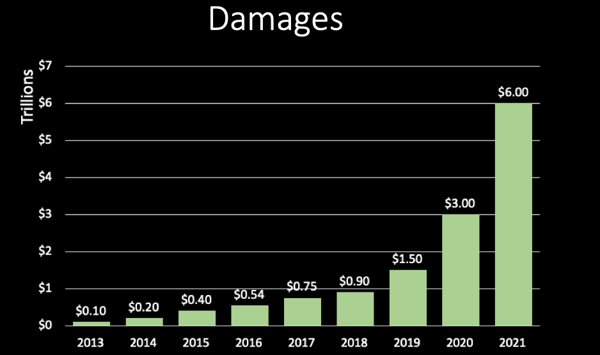
This is a chart illustrating the massive increase in volume and damages from cyber attacks. The chart includes data from 2013 to 2019, and an estimate through 2021 (from a report by Cybersecurity Ventures.) This indicates a four-x times multiple over just the next two years, from a $1.5 trillion dollar base in 2019.
Let's pause for a minute here and look at this number, which is now labeled as the greatest transfer of wealth in history and started as a paper written by Steve Morgan of Cybersecurity Ventures, considered the world's leading researcher and page-one for the global cyber economy. The outlook has stood for two years and the six trillion dollar number corroborated by hundreds of major media outlets, academia, senior government officials, associations, industry experts, and the largest cybersecurity players in the industry.
That brings us to the final piece of understanding the risk, which is perpetrators.
As the nature of cyberattacks has shifted from primarily a black hat, institutional concern, to cybercrime for-profit victimizing small, unprotected and vulnerable targets, perpetrators now range from common criminals and street thugs, to organized crime cartels, and re-engineered traditional crime syndicates.

Now that we have a deeper understanding of the nature of cyber risk today, let's go to the next part of our two-track approach; mitigating the risk.
To be effective at cyber risk mitigation, it's imperative to recognize the personalization of cyber risk. Today, the juncture of your greatest risk is at the intersection of people and the technology they use every day.
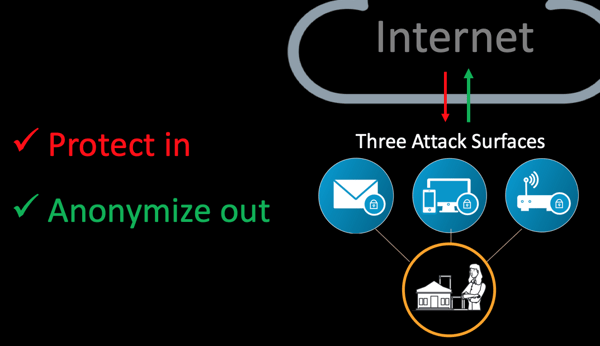
When helping others incorporate advanced cybersecurity in to their professional practices and daily lives, we start with these components we call the "Three Primary Cyber Attack Surfaces."

The two mandates for information security are to "Protect in, and encrypt out"
In simplistic terms, cybersecurity is about protecting from outside threats getting in, and securing information and communications as they go out. Simple to say but doing it can be complex, especially considering users are mobile and using powerful devices over public and private networks.
Here, I'm going to interject with this slide about an important element to today's presentation. It's the flip side of the bad news; innovation in cybersecurity is on fire.
The IT-security industry was a relatively sleepy oligopoly until 2012 when the world's capital markets suddenly understood cybercrime would be a dominant growth industry for the years ahead.
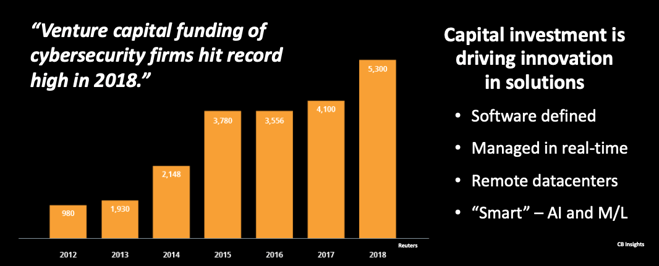
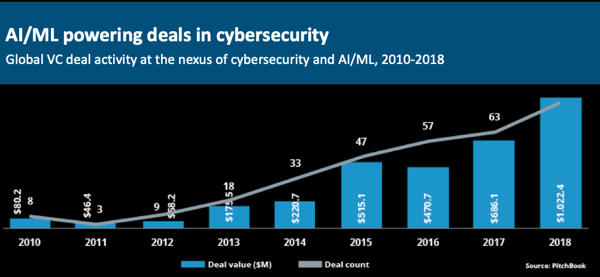
Smart innovators with solid funding are transforming the industry, and consumers are benefiting from solutions that are software-defined, remotely monitored, and managed, "smart", with artificial intelligence and machine learning. Systems are continually informed by collaborative threat intelligence from around the world, including data from government agencies, law enforcement, industry-specific intelligence, and third-party threat intel aggregators.
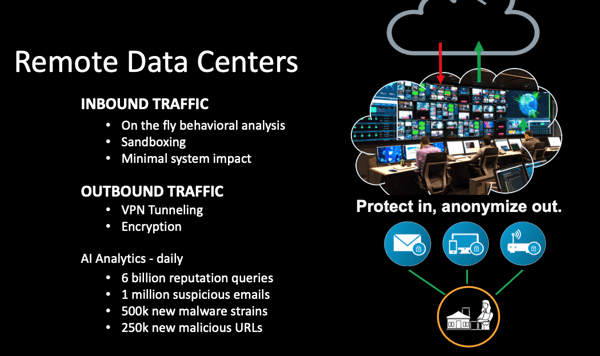
Modern cybersecurity technology uses remotely located data center, or an "IT security center in the cloud" to filter, scan, analyze, and clean inbound information from the Internet to our email, devices, and networks. All outbound traffic out to the Internet is tunneled and encrypted over a private VPN network. The effect is to avoid the hostile Internet and anonymize all outgoing information and communications - essentially making all of your activity invisible to the outside.
This brings us to the fundamentals, or what we call "The Four Fundamentals of Cybersecurity for Life."
But before I let you go, there's one more thing.
If cyber risk has been personalized, then we can't escape that people are the weakest link in the chain of defense.
It is imperative that as leaders, professionals, parents. and influencers that we provide those around us with the knowledge and tools they need to develop new life skills and find their personal path to survival and success in the new digital age.
This concludes my presentation for today. Thank you for your attention.
I'm Brad Deflin from Total Digital Security.
5 min read
When we introduced our OmniNet Bridge solution in 2014—known to many of you as My Digital Shield—it represented the next generation of network...

9 min read
Over the past decade writing these letters, I’ve made it my mission to help you navigate the digital age with confidence and resilience. If I have...

4 min read
For generations, family offices and ultra-high net worth families have mastered the art of estate planning — preserving wealth, ensuring succession,...